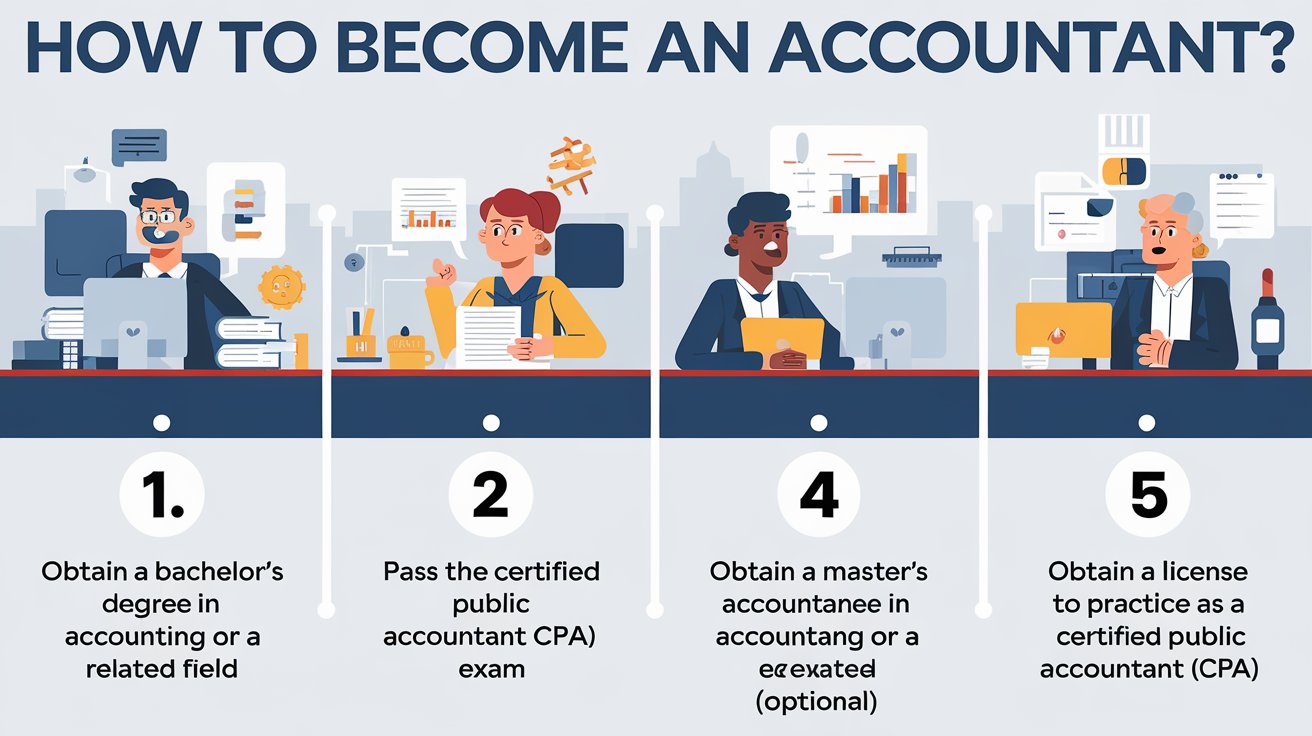
Effective Ways to Become an Accountant in 2025: Smart Strategies for Success

Embarking on a career as an accountant can be a rewarding and lucrative path for individuals who possess strong analytical skills and a passion for financial management. With the demand for skilled professionals in the accounting field increasing each year, 2025 presents unique opportunities for aspiring accountants. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about how to become an accountant by discussing essential accounting courses, certifications, skills, and tips for success.
The Foundation: Understanding Accounting Basics
Before diving into specific steps to become an accountant, it’s critical to understand the accounting basics. At its core, accounting involves the process of recording, classifying, and evaluating financial transactions to provide useful information for decision-making. An understanding of fundamental principles, including financial statements, bookkeeping, and cost accounting, is imperative for a successful career.
What Does an Accountant Do?
An accountant plays a vital role in any organization by managing financial records and ensuring compliance with various regulations. Typical responsibilities include preparing financial reports, assisting with taxation matters, and conducting audits. They also help organizations in budgeting and financial analysis, critical tasks for planning and forecasting financial stability. Understanding the breadth of this role can sharpen your focus on the skills and knowledge necessary to excel.
Key Accounting Skills for Success
Every aspiring accountant should develop a thorough understanding of the key accountant skills needed in the industry. These include proficiency in **accounting software**, analytical thinking, accuracy, and strong written and verbal communication skills. Additionally, grasping advanced skills like tax preparation and financial management can open doors for advanced positions within the field. Emerging areas such as **forensic accounting** and **financial technology** are also gaining traction, allowing accountants to diversify their expertise.
Pathways to Accounting Knowledge
One of the most effective ways to learn accounting is through structured educational programs. Pursuing an accounting degree, whether through a community college or a university, lays a robust foundation for your career. For those considering flexible learning options, enrolling in online accounting courses can offer the necessary knowledge at your own pace, catering to various learning styles and schedules.
Achieving Credentials: Accounting Certifications
While a degree serves as a great starting point, obtaining professional certification can greatly enhance your career prospects. The most recognized credential in the field is the **Certified Public Accountant (CPA)** designation, which signifies expertise in accounting principles and practices. Studying for the **CPA exam** involves understanding complex regulations and ethical considerations inherent in accounting, preparing you for responsibilities that extend beyond basic financial statements.
Other Relevant Certifications
In addition to the CPA certification, pursuing other specialized accounting certifications can be advantageous. These include certifications in taxation, financial planning, or forensic accounting. Each credential requires specific training and assessment, further establishing your credibility and enhancing your marketability in a competitive job environment.
Continuing Education and Professional Development
The field of accounting is ever-evolving, making it vital to engage in continual professional development. This includes attending workshops, webinars, and industry conferences offered by professional accounting organizations. Staying abreast of accounting industry trends such as financial regulations and evolving compliance issues ensures that you remain relevant and competitive in the job market.
Networking and Mentorship Opportunities
Gaining insight from established professionals in your field is an invaluable resource. Participating in networking opportunities can build connections that lead to job openings and mentorship experiences. Engaging with organizations dedicated to accountants not only helps expand your professional network but can also provide support and career advancement strategies tailored for you.
Practical Steps to Gain Experience
Gaining practical experience is essential to transitioning from academic learning to a professional accounting career. Consider internships within accounting firms or positions as an entry-level accountant. These opportunities allow you to apply what you’ve learned in real-world environments while establishing connections within the industry.
Applying for Accounting Internships
Pursuing internships can serve as an ideal stepping stone. Whether offered through colleges or found by reaching out to local businesses, accounting internships provide exposure to daily tasks such as verifying accounts payable and accounts receivable transactions. Hands-on experience can clarify career interests and lay the necessary groundwork for future roles.
Building an Impressive Accountant Resume
Crafting an effective resume tailored to accounting roles can differentiate you from other candidates. Include relevant skills, education, internships, and any certifications you’ve achieved. Highlighting accountant responsibilities, such as financial reporting or budgeting tasks, can demonstrate your ability to execute essential duties expected of this job.
Cracking the Interview Code
Preparing for interviews is equally important in securing a position. Familiarize yourself with common interview questions for accountants and be ready to discuss how your educational background and experiences align with the accountant job description. Researching the company you are applying to and understanding its financial position demonstrates your proactive approach and commitment to being the right fit for the organization.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the importance of fundamental accounting principles and skills.
- Consider obtaining relevant certifications such as CPA for career advancement.
- Pursue practical experience through internships and volunteer opportunities.
- Engage in continuous education to stay updated with industry changes.
- Build a strong professional network for mentorship and job opportunities.
FAQ
1. What is the best degree for becoming an accountant?
The best degree is typically a bachelor’s degree in accounting or finance. However, pursuing a master’s degree can enhance job opportunities and prepare you for obtaining CPA certification.
2. Can I become an accountant without a degree?
While having a degree significantly improves your chances, you can begin your journey through community college programs and eventually acquire certifications, such as accounting certificates, along with relevant experience.
3. What skills do I need to succeed in accounting?
Essential skills include analytical thinking, proficiency in accounting software, attention to detail, and strong communication abilities. Being well-versed in financial regulations and taxation is equally crucial.
4. What certifications are valuable for accountants?
Common certifications that add value to accounting professionals include CPA, CMA (Certified Management Accountant), and CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst). Each credential can increase your employability and salary potential.
5. How to prepare for the CPA exam?
Preparing for the CPA exam involves studying key accounting concepts, and possibly enrolling in CPA review courses, while forming study groups can enhance learning and retention of the material.
6. Are there online options for accounting courses?
Yes! There are numerous online resources and accounting programs that offer courses covering various topics, from basic accounting practices to advanced financial management.
7. What are some career paths in accounting?
Career paths in accounting include public accounting, management accounting, tax accounting, forensic accounting, and internal auditing, each offering unique responsibilities and specialties.