“`html
Effective Ways to Calculate the Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism
Understanding the Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism
The **surface area of a rectangular prism** is an essential concept in **geometry** that quantifies the total area of the prism’s faces. To successfully **calculate surface area**, you need to understand the **rectangular prism dimensions**, which refer to length, width, and height. The surface area formula is derived based on these dimensions, highlighting the connection between 3D shapes and their geometry-related calculations. For general explorations of the topic, the formula for the surface area— **SA = 2lw + 2lh + 2wh**—is vital. Here “l” is the length, “w” is the width, and “h” is the height. Utilizing these measurements effectively allows for various practical applications including construction, material estimation, and real-world projects.
The Formula for Surface Area: Breakdown and Explanation
To **find surface area** accurately, it’s necessary to break down the **surface area calculation** into manageable parts. The surface area can be calculated by summing the areas of all six faces of the prism. Each pair of opposite faces has the same dimensions, meaning: two faces correspond to the length and width (**lw**), two to the length and height (**lh**), and two to the width and height (**wh**). A practical application of this involves considering a rectangular box with dimensions 3 cm (width), 4 cm (length), and 5 cm (height). Plugging these values into the formula leads us to calculate **SA = 2(3*4) + 2(4*5) + 2(3*5)**, yielding a final surface area of 94 cm². This approach illustrates the ease of using the formula to make straightforward calculations.
Real-World Applications of Surface Area Calculations
Understanding the **surface area calculations** is crucial for various practical demands. **Surface area units** are paramount when assessing material costs or quantities needed for painting or wrapping objects. For example, if your task is to paint a rectangular prism, such as a storage box, calculating its surface area will give you a precise understanding of how much paint you will require. Additionally, in disciplines such as engineering or architecture, accurately calculating **rectangular prism surface area** helps in analyzing costs, enhancing designs, and ensuring proper assembly of components. Using surface area effectively promotes smart decision-making in projects, contributing to efficient resource management.
The Steps to Calculate Surface Area Efficiently
Calculating the surface area of a rectangular prism can seem daunting, but breaking it down into **steps to calculate surface area** can simplify the task. Start by measuring the necessary **length width height** dimensions using appropriate **measuring techniques**. It’s important to ensure that all the measurements are in the same unit of measurement to maintain accuracy. After that, apply the surface area formula step by step. First, compute the area of one set of parallel faces, then move on to the next set, followed by the last. Finally, sum all the computed areas to arrive at the total **surface area**. This systematic approach makes the surface area calculations not only effective but easy to follow for learners and educators alike.
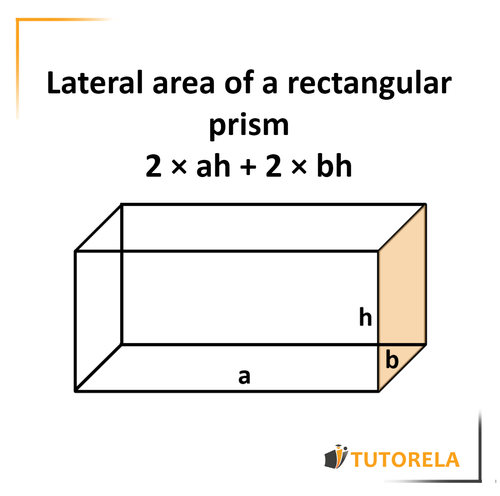
Visualizing Rectangular Prisms for Better Understanding
One of the most effective techniques for teaching geometry is **visualizing rectangular prisms** using diagrams or models. For example, utilizing images, such as the ones shown below, can help students grasp the spatial relationships between length, width, and height, as well as the properties of **geometric figures** in 3D forms. Providing pupils with hands-on opportunities to measure physical objects can also enhance their engagement and understanding of calculating surface areas. Such methods build a solid foundation in teaching vital geometric concepts and develop spatial reasoning skills necessary for comprehending dimensions and their applications in real life.
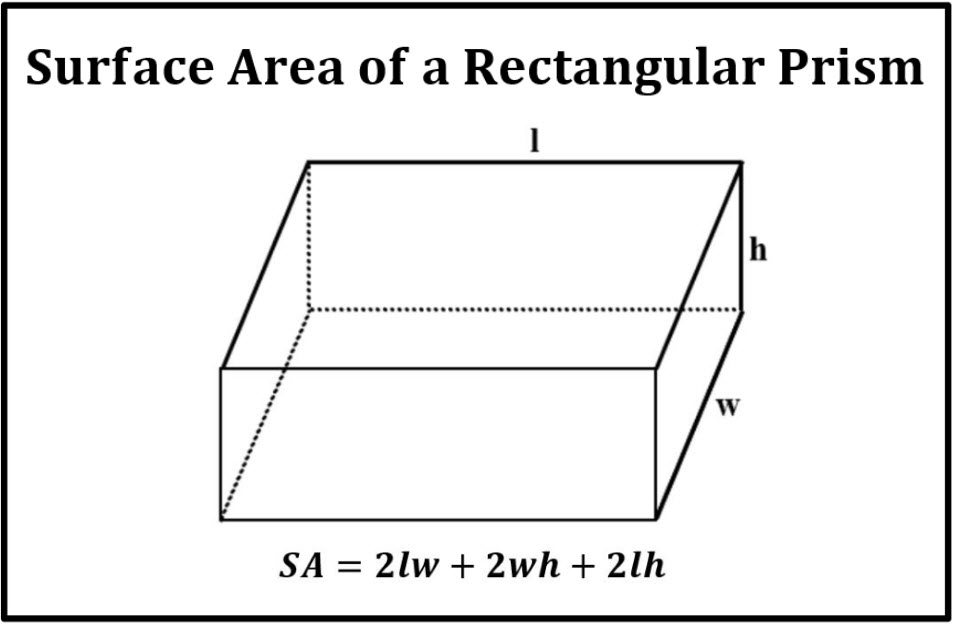
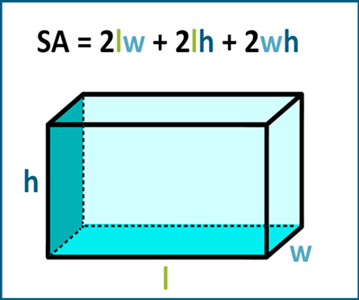
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Finding Surface Area
While calculating the surface area, it’s essential to avoid several **common mistakes**. These can include misreading measurements, not using consistent units, or misapplying the surface area formulas. For example, assuming certain dimensions as equal in calculations when they aren’t can lead to discrepancies. Additionally, one must remember to multiply the area of each pair of sides by two, as there are two identical faces on each dimension. By acknowledging and learning from these typical errors, students and professionals alike can enhance their calculation skills and deepen their understanding.
Differences Between Surface Area and Volume
It’s important to differentiate between **volume vs surface area**, especially in geometry. While the **surface area** provides insight into the total area exposed, volume measures how much space the prism occupies. The formulas diverge significantly, with volume calculated as **V = lwh**. Understanding these distinctions aids learners in applying the right geometric principles to their calculations. Additionally, exploring still further into the relationship between these two concepts can yield insights into environments where maximizing volume is crucial, like storage optimizations in logistics or architectural designs.
Educational Resources for Teaching Surface Area
To enrich the learning experience in understanding the **mathematical concept of area**, teachers can utilize various **educational resources**, including worksheets, visual aids, and hands-on projects. Websites offering interactive geometry tools or simulation software can add depth to traditional teachings. Moreover, engaging students with computer-aided design projects presents the information dynamically, enabling students to apply surface area calculations directly to real-world scenarios. This approach not only fosters conceptual understanding but also promotes creativity and critical thinking among students.
Developing Practical Problem-Solving Skills in Geometry
Incorporating **practical problem-solving** techniques in lessons on calculating surface area can significantly aid students in grasping complex geometric principles. For example, working through real-life examples and scenarios—like calculating paint coverage for a home renovation project—demonstrates the practical application of geometry. Encouraging iterative problem-solving allows students to see multiple growth opportunities in applying **geometry** effectively. Real-world applications increase motivation and establish a connection to the mathematical principles being taught.
Key Takeaways
- The surface area of a rectangular prism provides total exposure measurement, essential for various practical calculations.
- Applying the formula SA = 2lw + 2lh + 2wh allows for straightforward breakdown of complex calculations.
- Visualization and practical engagements enhance understanding of surface area in geometric contexts.
- Distinguishing between surface area and volume is vital for accurate geometric comprehension.
- Utilizing educational resources can make learning engaging while fostering deeper understanding of geometric principles.
FAQ
1. How do you visualize the surface area of a rectangular prism?
Visualizing the surface area involves creating diagrams or using physical models to represent the rectangular prism. This could include drawing the prism and labeling each face or manipulating 3D models to see how changes in dimensions affect surface area. Enhancing spatial awareness leads to better understanding, enabling learners to grasp complex geometric relationships.
2. What is the importance of surface area calculations in real-life applications?
Surface area calculations are crucial in various fields such as construction, manufacturing, and packaging. For example, determining the required amount of material for wrapping or painting items is dependent on accurate surface area measurements. This promotes efficiency and cost-effectiveness in real-world projects, underscoring why these calculations matter.
3. Can surface area be applied to irregular shapes?
While **surface area** calculations are widely utilized for regular shapes like rectangular prisms, irregular shapes can be measured using approximations or techniques such as 3D modeling or breaking the shape down into simpler components. This enhances understanding of applying geometric principles flexibly across diverse shapes encountered in various contexts.
4. What techniques can be used for teaching surface area effectively?
Effective teaching methods for surface area include interactive learning experiences, such as hands-on activities, using computer-aided design software, and visual aids to illustrate complexities. Engaging students in problem-solving further develops their skills, allowing them to understand and apply formulas dynamically in practical contexts.
5. How can understanding surface area impact architectural design?
Architects utilize surface area calculations to assess material requirements and design efficiencies in their plans. Understanding how surface area impacts elements like thermal resistance or material costs assists architects in making informed decisions to optimize their designs, thereby influencing energy efficiency and the overall sustainability of their projects.
“`